In this tutorial, we will learn how to write unit tests for the Spring Boot application using Junit 5 and Mockito.
Spring Boot provides different testing approaches, such as Unit Testing, Integration Testing, and End-to-End Testing. In this tutorial, we will learn how to write unit tests for the Spring Boot application.

Prerequisites
- Good Knowledge of Java.
- Good Understanding of Spring Boot.
- Good Understanding of MySQL workbench and IDE (In this project I have used Intellij IDE).
Required Technologies and Apps
- Java ( latest JDK 17 or above )
- Spring Boot project file.
- Intellij IDE
- Postman
- MySQL Workbench
Download Source Code from Github — Download Source Code
What is Unit Testing ?
Unit testing is a software testing technique where individual units or components of a software application are tested in isolation to verify that they perform as expected.
Spring Boot Starter Test Dependency
The Spring Boot Starter Test dependency provides essential libraries and utilities for testing Spring Boot applications, including JUnit, Hamcrest, Mockito, and AssertJ. It simplifies the process of writing and executing tests for Spring Boot applications.
What is JUnit ?
JUnit is a popular open-source testing framework for Java. It provides annotations to define test methods, test classes, and test suites, along with assertions for verifying expected outcomes. JUnit makes it easy to write and execute unit tests, ensuring the correctness of Java code.
What is AssertJ Library?
AssertJ is a popular Java library that provides fluent, expressive assertions for writing clearer and more readable unit tests. And also It provides helpful error messages.
Set up the Projet
First, we need to make crud application.
3. Make a project file with the spring initializer tool.
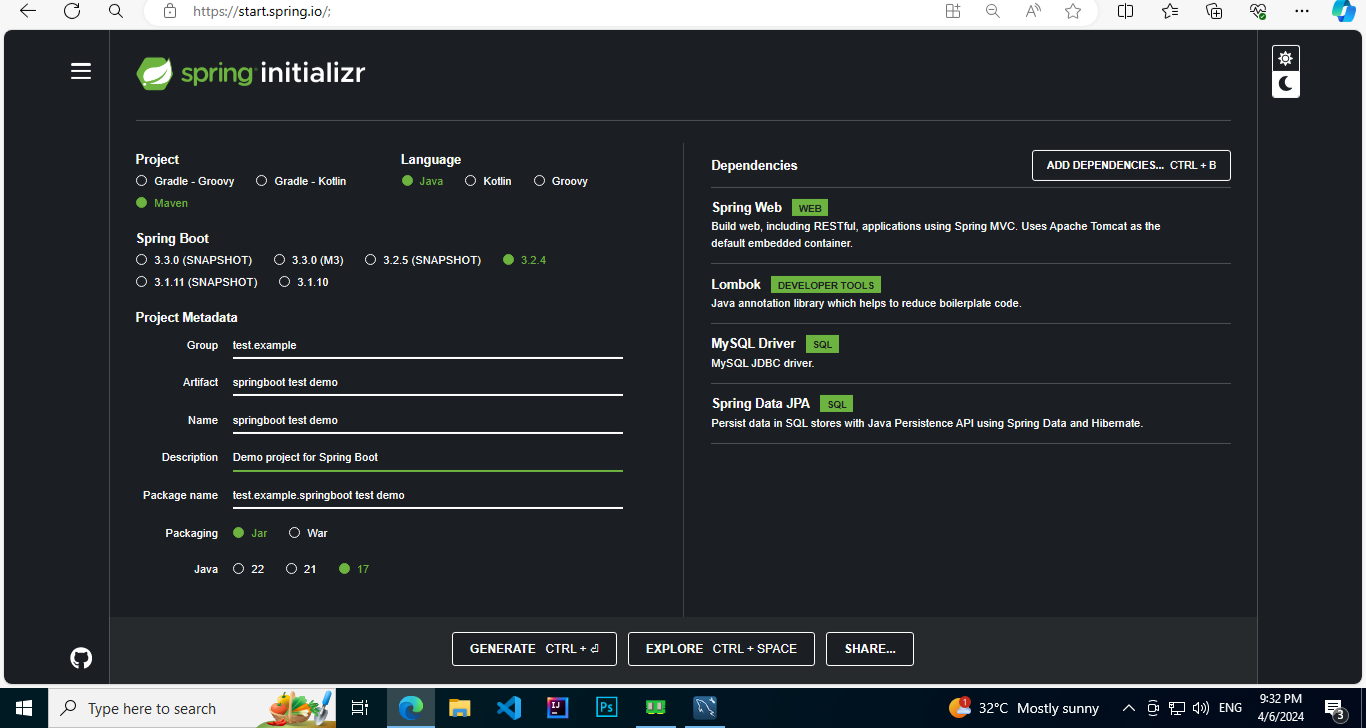
Download the project and Open Project from IntelliJ.
2. Make the project structure.

3. Add class and interfaces.
Application.Properties File
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/unit_test_db?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=Online12@
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = updateEmployee Entity class
package test.example.springboot.test.demo.Model;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.*;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String firstName;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String lastName;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String email;
}Employee Repository
package test.example.springboot.test.demo.Repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Model.Employee;
import java.util.Optional;
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long> {
Optional<Employee> findByEmail(String email);
}Employee Controller
package test.example.springboot.test.demo.Controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Model.Employee;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Service.EmployeeService;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/employees")
public class EmployeeController {
private EmployeeService employeeService;
public EmployeeController(EmployeeService employeeService) {
this.employeeService = employeeService;
}
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public Employee createEmployee(@RequestBody Employee employee){
return employeeService.saveEmployee(employee);
}
@GetMapping
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees(){
return employeeService.getAllEmployees();
}
@GetMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Optional<Employee>> getEmployeeById(@PathVariable("id") long id){
return new ResponseEntity<Optional<Employee>>(employeeService.getEmployeeById(id),HttpStatus.OK);
}
@PutMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Employee> updateEmployee(@PathVariable("id") long id,
@RequestBody Employee employee){
return new ResponseEntity<Employee>(employeeService.updateEmployee(employee,id),HttpStatus.OK);
}
@DeleteMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity<String> deleteEmployee(@PathVariable("id") long id){
employeeService.deleteEmployee(id);
return new ResponseEntity<String>("Employee deleted successfully!.", HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
Employee Service
package test.example.springboot.test.demo.Service;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Model.Employee;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
public interface EmployeeService {
Employee saveEmployee(Employee employee);
List<Employee> getAllEmployees();
Optional<Employee> getEmployeeById(long id);
Employee updateEmployee(Employee employee,long id);
void deleteEmployee(long id);
}Service Implementation
package test.example.springboot.test.demo.Service.Impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Model.Employee;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Repository.EmployeeRepository;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Service.EmployeeService;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
@Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService {
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
public EmployeeServiceImpl(EmployeeRepository employeeRepository) {
this.employeeRepository = employeeRepository;
}
@Override
public Employee saveEmployee(Employee employee) {
Optional<Employee> savedEmployee = employeeRepository.findByEmail(employee.getEmail());
if(savedEmployee.isPresent()){
throw new RuntimeException("Employee already exist with given email:" + employee.getEmail());
}
return employeeRepository.save(employee);
}
@Override
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees() {
return employeeRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public Optional<Employee> getEmployeeById(long id) {
return employeeRepository.findById(id);
}
@Override
public Employee updateEmployee(Employee employee,long id) {
Employee existingEmployee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(()->new RuntimeException());
existingEmployee.setFirstName(employee.getFirstName());
existingEmployee.setLastName(employee.getLastName());
existingEmployee.setEmail(employee.getEmail());
employeeRepository.save(existingEmployee);
return existingEmployee;
}
@Override
public void deleteEmployee(long id) {
employeeRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
4. Test application Using Postman
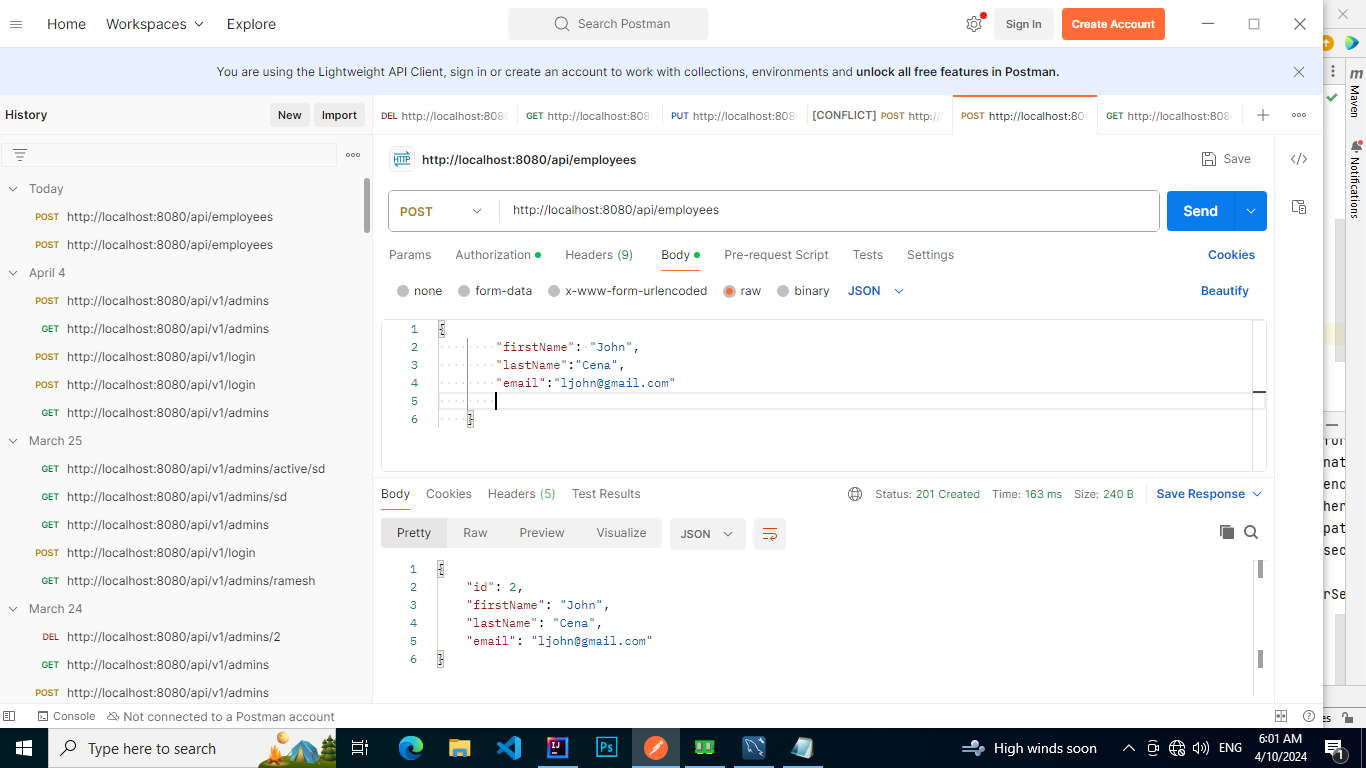
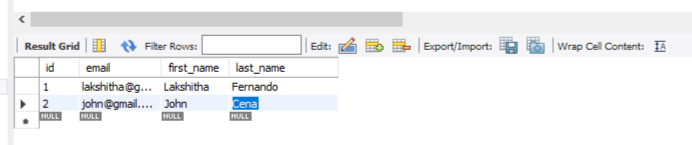
This way, you can test all your APIs. And also, I saved two employees.
Let’s write the unit test for the repository layer with JUnit (Don’t need Mockito)

Open EmployeeRepositoryUnitTest.java class.
package test.example.springboot.test.demo.Repository;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.DataJpaTest;
import org.springframework.test.annotation.Rollback;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Model.Employee;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
@DataJpaTest
@TestMethodOrder(MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation.class)
public class EmployeeRepositoryUnitTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@Test
@DisplayName("Test 1:Save Employee Test")
@Order(1)
@Rollback(value = false)
public void saveEmployeeTest(){
//Action
Employee employee = Employee.builder()
.firstName("Sam")
.lastName("Curran")
.email("sam@gmail.com")
.build();
employeeRepository.save(employee);
//Verify
System.out.println(employee);
Assertions.assertThat(employee.getId()).isGreaterThan(0);
}
@Test
@Order(2)
public void getEmployeeTest(){
//Action
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(1L).get();
//Verify
System.out.println(employee);
Assertions.assertThat(employee.getId()).isEqualTo(1L);
}
@Test
@Order(3)
public void getListOfEmployeesTest(){
//Action
List<Employee> employees = employeeRepository.findAll();
//Verify
System.out.println(employees);
Assertions.assertThat(employees.size()).isGreaterThan(0);
}
@Test
@Order(4)
@Rollback(value = false)
public void updateEmployeeTest(){
//Action
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(1L).get();
employee.setEmail("samcurran@gmail.com");
Employee employeeUpdated = employeeRepository.save(employee);
//Verify
System.out.println(employeeUpdated);
Assertions.assertThat(employeeUpdated.getEmail()).isEqualTo("samcurran@gmail.com");
}
@Test
@Order(5)
@Rollback(value = false)
public void deleteEmployeeTest(){
//Action
employeeRepository.deleteById(1L);
Optional<Employee> employeeOptional = employeeRepository.findById(1L);
//Verify
Assertions.assertThat(employeeOptional).isEmpty();
}
}
@TestMethodOrder(MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation.class) specify the order of test execution based on the order specified by the @Order annotation.
Note:
You can use MySQL or any other database for your project to save the actual data. If you use the same database for testing, it will affect your actual data. So, you can use the in-memory H2 database for testing. It is the common way.
Add H2 dependency to pom.xml file.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>Change the application.properties file.
#MysQL Database Configuration for Project
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/unit_test_db?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=Online12@
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
#H2 Database Configuration for testing
spring.datasource.test.url=jdbc:h2:mem/unit_test_db
spring.datasource.test.diver-class-name=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.test.username=sa
spring.datasource.test.password=password
spring.jpa.test.hibernate.ddl-auto = create-dropRun the EmployeeRepositoryUnitTest.java class.
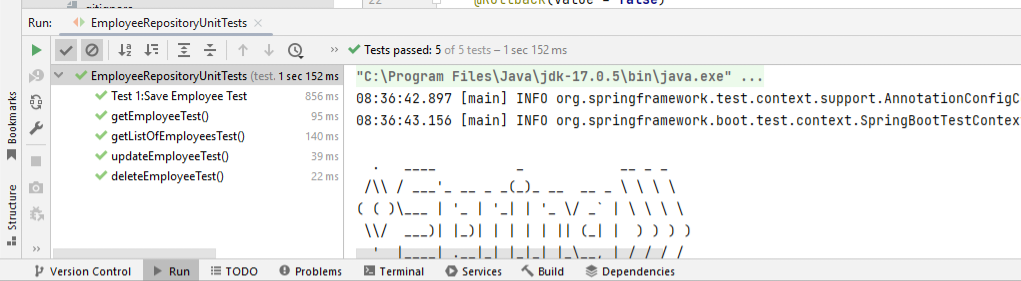
Let’s write the unit test for controller layer with JUnit 5 and Mockito
What is Mockito?
Mockito is a popular Java framework used for mocking objects in unit tests. Mockito can be used in unit tests to mock dependencies and isolate the code being tested.
Controllers often depend on service layer components to perform business logic or interact with the application’s data layer (e.g., repositories). Mock the service layer components using Mockito to isolate the controller being tested from the actual service layer implementation.
What is MockMvc?
MockMvc is not part of Mockito. MockMvc is a class provided by the Spring Test framework specifically for testing Spring MVC controllers.
Open EmployeeControllerUnitTests class
package test.example.springboot.test.demo.Controller;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultActions;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Model.Employee;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Service.EmployeeService;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import static org.mockito.BDDMockito.*;
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.is;
import static org.mockito.ArgumentMatchers.any;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultHandlers.print;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@WebMvcTest(EmployeeController.class)
@TestMethodOrder(MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation.class)
public class EmployeeControllerUnitTests {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@MockBean
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
Employee employee;
@BeforeEach
public void setup(){
employee = Employee.builder()
.id(1L)
.firstName("John")
.lastName("Cena")
.email("john@gmail.com")
.build();
}
//Post Controller
@Test
@Order(1)
public void saveEmployeeTest() throws Exception{
// precondition
given(employeeService.saveEmployee(any(Employee.class))).willReturn(employee);
// action
ResultActions response = mockMvc.perform(post("/api/employees")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(employee)));
// verify
response.andDo(print()).
andExpect(status().isCreated())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.firstName",
is(employee.getFirstName())))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.lastName",
is(employee.getLastName())))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.email",
is(employee.getEmail())));
}
//Get Controller
@Test
@Order(2)
public void getEmployeeTest() throws Exception{
// precondition
List<Employee> employeesList = new ArrayList<>();
employeesList.add(employee);
employeesList.add(Employee.builder().id(2L).firstName("Sam").lastName("Curran").email("sam@gmail.com").build());
given(employeeService.getAllEmployees()).willReturn(employeesList);
// action
ResultActions response = mockMvc.perform(get("/api/employees"));
// verify the output
response.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.size()",
is(employeesList.size())));
}
//get by Id controller
@Test
@Order(3)
public void getByIdEmployeeTest() throws Exception{
// precondition
given(employeeService.getEmployeeById(employee.getId())).willReturn(Optional.of(employee));
// action
ResultActions response = mockMvc.perform(get("/api/employees/{id}", employee.getId()));
// verify
response.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.firstName", is(employee.getFirstName())))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.lastName", is(employee.getLastName())))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.email", is(employee.getEmail())));
}
//Update employee
@Test
@Order(4)
public void updateEmployeeTest() throws Exception{
// precondition
given(employeeService.getEmployeeById(employee.getId())).willReturn(Optional.of(employee));
employee.setFirstName("Max");
employee.setEmail("max@gmail.com");
given(employeeService.updateEmployee(employee,employee.getId())).willReturn(employee);
// action
ResultActions response = mockMvc.perform(put("/api/employees/{id}", employee.getId())
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(employee)));
// verify
response.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.firstName", is(employee.getFirstName())))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.email", is(employee.getEmail())));
}
// delete employee
@Test
public void deleteEmployeeTest() throws Exception{
// precondition
willDoNothing().given(employeeService).deleteEmployee(employee.getId());
// action
ResultActions response = mockMvc.perform(delete("/api/employees/{id}", employee.getId()));
// then - verify the output
response.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andDo(print());
}
}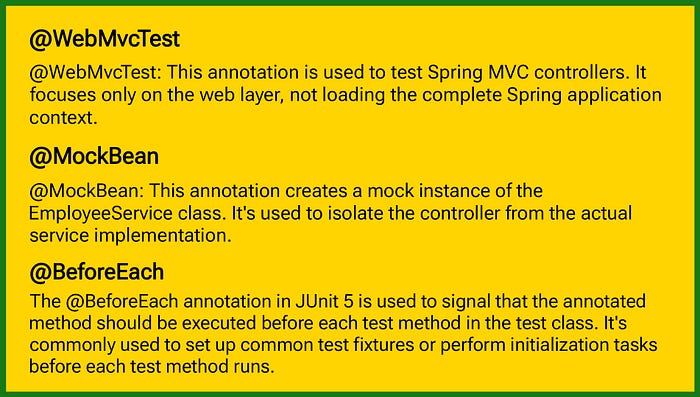
ObjectMapper class is used for converting Java objects to JSON and vice versa.
given: This method is part of the Mockito framework. It is used to specify a precondition or setup for the test.
Run the test class.
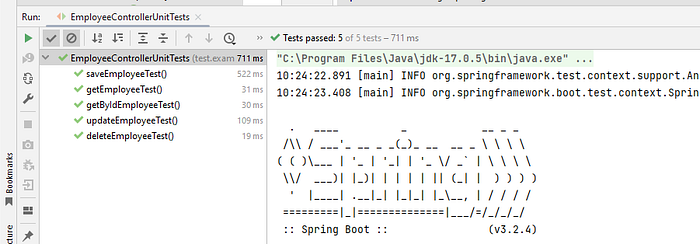
Let’s write the unit test for service layer with JUnit and Mockito
Open EmployeeServiceUnitTests class
package test.example.springboot.test.demo.Service;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.mockito.InjectMocks;
import org.mockito.Mock;
import org.mockito.junit.jupiter.MockitoExtension;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Model.Employee;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Repository.EmployeeRepository;
import test.example.springboot.test.demo.Service.Impl.EmployeeServiceImpl;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
import static org.mockito.BDDMockito.given;
import static org.mockito.BDDMockito.willDoNothing;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.verify;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.times;
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
@TestMethodOrder(MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation.class)
public class EmployeeServiceUnitTests {
@Mock
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@InjectMocks
private EmployeeServiceImpl employeeService;
private Employee employee;
@BeforeEach
public void setup(){
employee = Employee.builder()
.id(1L)
.firstName("John")
.lastName("Cena")
.email("john@gmail.com")
.build();
}
@Test
@Order(1)
public void saveEmployeeTest(){
// precondition
given(employeeRepository.save(employee)).willReturn(employee);
//action
Employee savedEmployee = employeeService.saveEmployee(employee);
// verify the output
System.out.println(savedEmployee);
assertThat(savedEmployee).isNotNull();
}
@Test
@Order(2)
public void getEmployeeById(){
// precondition
given(employeeRepository.findById(1L)).willReturn(Optional.of(employee));
// action
Employee existingEmployee = employeeService.getEmployeeById(employee.getId()).get();
// verify
System.out.println(existingEmployee);
assertThat(existingEmployee).isNotNull();
}
@Test
@Order(3)
public void getAllEmployee(){
Employee employee1 = Employee.builder()
.id(2L)
.firstName("Sam")
.lastName("Curran")
.email("sam@gmail.com")
.build();
// precondition
given(employeeRepository.findAll()).willReturn(List.of(employee,employee1));
// action
List<Employee> employeeList = employeeService.getAllEmployees();
// verify
System.out.println(employeeList);
assertThat(employeeList).isNotNull();
assertThat(employeeList.size()).isGreaterThan(1);
}
@Test
@Order(4)
public void updateEmployee(){
// precondition
given(employeeRepository.findById(employee.getId())).willReturn(Optional.of(employee));
employee.setEmail("max@gmail.com");
employee.setFirstName("Max");
given(employeeRepository.save(employee)).willReturn(employee);
// action
Employee updatedEmployee = employeeService.updateEmployee(employee,employee.getId());
// verify
System.out.println(updatedEmployee);
assertThat(updatedEmployee.getEmail()).isEqualTo("max@gmail.com");
assertThat(updatedEmployee.getFirstName()).isEqualTo("Max");
}
@Test
@Order(5)
public void deleteEmployee(){
// precondition
willDoNothing().given(employeeRepository).deleteById(employee.getId());
// action
employeeService.deleteEmployee(employee.getId());
// verify
verify(employeeRepository, times(1)).deleteById(employee.getId());
}
}
Run the class
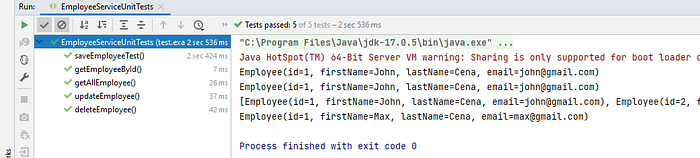
Summary
In this tutorial we have written Spring Boot unit testing for Repositories, Controllers and Services using JUnit 5 and Mockito.
Integration Testing
Many experienced programmers and teams prioritize both Unit and Integration testing to ensure robust, reliable, and maintainable applications.
If you like, you can learn integration testing. My Integration Testing artical —https://medium.com/@Lakshitha_Fernando/integration-testing-bb31676915ae
